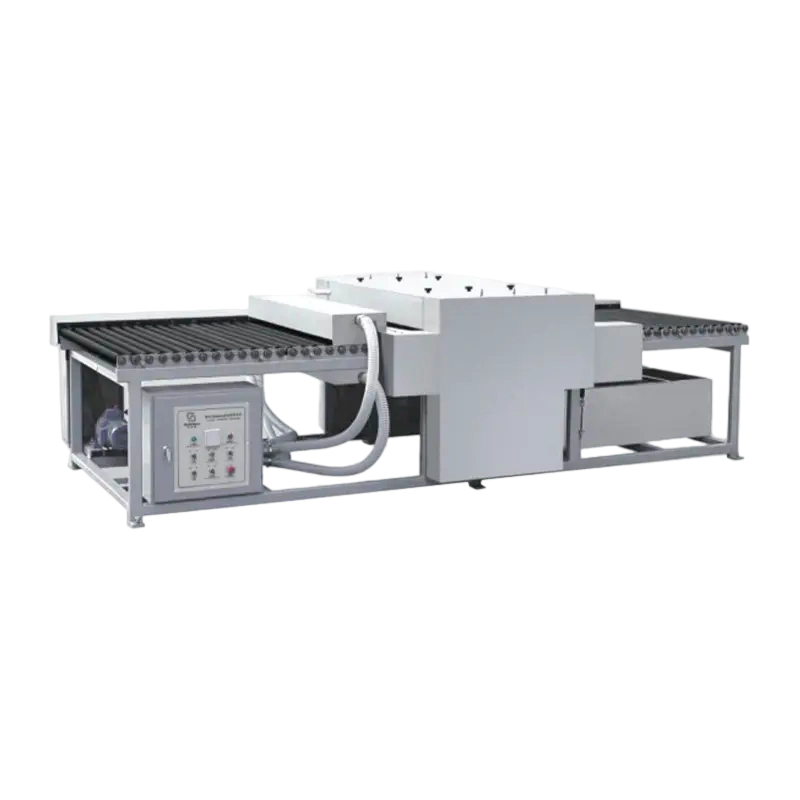
In the modern manufacturing landscape, precision, efficiency, and versatility are paramount. For industries ranging from automotive to architecture, the ability to cut, shape, and finish glass with high accuracy is a critical requirement. This is where advanced CNC Glass Processing Equipment comes into play. These computer-numerically-controlled machines have revolutionized glass fabrication, enabling complex designs, tight tolerations, and automated production. Jiangyin Jingang Nonwoven Co., Ltd., with over 26 years of expertise in developing specialized machinery, has been at the forefront of this innovation, particularly with our independently designed CNC edging machines for shaped glass. This guide delves deep into the world of CNC glass processing, offering detailed insights to help you understand its capabilities and make informed decisions.
Understanding CNC Glass Processing Technology
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) glass processing involves using automated machinery guided by pre-programmed software to perform precise operations on glass. The core principle is subtractive manufacturing, where material is removed from a glass sheet to achieve the desired shape, edge, or hole.
Core Components of a CNC Glass Machine
A typical system comprises several integrated parts:
- Control System: The brain of the operation, using CAD/CAM software to translate designs into machine commands (G-code).
- Mechanical Structure: A robust frame (often granite or steel) that ensures stability and minimizes vibration during high-speed operations.
- Spindle & Tooling: A high-speed spindle holds various diamond tools for cutting, grinding, drilling, and polishing.
- Cooling System: Essential for lubricating the cutting area, reducing heat, and flushing away glass dust to extend tool life and ensure edge quality.
- Handling System: May include loaders, conveyors, or robotic arms for automating material flow.
Key Operational Processes
The equipment executes a sequence of processes:
- Scoring & Cutting: A diamond wheel scores the glass surface, followed by a break-out operation.
- Grinding & Edging: Rough edges are smoothed using diamond grinding wheels of progressively finer grits.
- Drilling & Milling: For creating holes or intricate contours.
- Polishing: Achieves a glossy, transparent edge finish using polishing wheels.
- Washing & Drying: Cleans the processed glass of coolant and debris.
Applications and Industries Served by CNC Glass Processing
The precision of CNC Glass Processing Equipment unlocks possibilities across diverse sectors. CNC machines for architectural glass are indispensable for creating custom facades, staircases, balustrades, and partitions with complex geometric shapes. In the automotive industry, the demand for automotive glass CNC cutting solutions is high for producing side windows, windshields, and sunroofs with exacting specifications for fit and safety. The electronics sector relies on precise CNC equipment for smartphone glass cutting to manufacture durable cover glass and touchscreens. Furthermore, the interior design and furniture markets utilize these machines for producing decorative glass panels, tabletops, and shelves, while the solar energy industry uses them to shape photovoltaic glass.
How to Choose the Right CNC Glass Processing Machine
Selecting the appropriate equipment is crucial for productivity and return on investment. Here is a detailed comparison of key selection factors, followed by a textual summary.
Critical Selection Factors Compared
Understanding the trade-offs between different machine specifications is essential.
Machine Specifications Comparison
| Factor | Option A (Standard Duty) | Option B (Heavy Duty/Precision) | Key Consideration |
| Machine Size & Load Capacity | Smaller worktable, lower load (e.g., <300kg) | Large format, high load capacity (e.g., >1000kg) | Dictates the maximum glass sheet size and thickness you can process. |
| Spindle Power & Speed | Lower power (e.g., 5-10kW), moderate RPM | High power (e.g., 15-30kW), high RPM (>12,000) | Affects cutting/grinding speed, ability to handle thick glass, and final edge quality. |
| Number of Axes | 3-axis (X, Y, Z) | 4-axis or 5-axis | 3-axis is for flat work; 4/5-axis enables complex 3D shaping and beveling. |
| Automation Level | Manual loading/unloading | Integrated automatic loading, unloading, and sorting | Directly impacts labor costs, throughput, and operational safety. |
| Control Software | Basic proprietary software | Advanced software with 3D simulation, nesting, and database management | Determines ease of programming, design flexibility, and material optimization. |
As shown in the table, the choice between a standard-duty and a heavy-duty machine hinges on production scale and product complexity. For high-volume production of simple flat glass, a robust 3-axis machine with automation might be ideal. For bespoke architectural projects involving shaped glass edging with CNC technology, a 5-axis machine becomes necessary. Furthermore, the importance of low-cost CNC glass engraving machines should not be overlooked for businesses entering the decorative glass market, where initial investment is a primary concern. A thorough evaluation of maintenance requirements for CNC glass cutters is also vital, as machines with easier access to components and reliable local technical support, like those offered by Jiangyin Jingang, minimize downtime and ensure long-term operational stability.
Advanced Techniques and Future Trends
The evolution of CNC Glass Processing Equipment is driven by demands for higher efficiency and new functionalities.
Integration with Smart Factories
- IoT Connectivity: Machines equipped with sensors for real-time monitoring of spindle health, tool wear, and production status.
- Data Analytics: Collecting operational data to predict maintenance needs (predictive maintenance) and optimize production schedules.
- Robotic Integration: Fully automated production cells where robots handle all material movement between CNC processing, washing, and inspection stations.
Innovations in Processing
- Laser-Assisted Cutting: Using lasers to thermally score glass before mechanical separation, resulting in smoother edges and reduced micro-cracks [1].
- Ultrasonic-Assisted Machining: Applying ultrasonic vibration to the cutting tool, which significantly reduces cutting force and improves edge quality on brittle materials like glass [2].
- Eco-Friendly Coolants: Development of water-based and biodegradable coolants to reduce environmental impact without compromising performance.
Research indicates that laser-assisted methods can reduce edge chipping by up to 60% compared to conventional mechanical scoring [1]. Similarly, ultrasonic-assisted machining has been shown to lower subsurface damage depth, which is critical for the structural integrity of load-bearing glass components [2].
Why Choose Jiangyin Jingang for Your CNC Glass Processing Needs?
With a legacy dating back to 1999, Jiangyin Jingang Nonwoven Co., Ltd. has built a reputation for engineering excellence and reliable manufacturing. Our journey into specialized machinery led to the successful launch of CNC edging machines for shaped glass in 2009, a milestone that expanded the application scope of glass processing. Our deep understanding of both materials and machinery allows us to offer unique insights.
- Proven Expertise: Over 26 years of dedicated R&D in industrial equipment, translating to robust and reliable machine design.
- Customization Focus: We understand that one size does not fit all. We offer flexible machine configurations to match specific production goals, whether for automotive glass CNC cutting solutions or intricate decorative work.
- Quality Assurance: A strict multi-stage inspection process ensures every machine component meets high-performance standards before assembly and delivery.
- Comprehensive Support: From initial consultation and installation to training and after-sales service, we partner with our clients for long-term success.
We are committed to providing not just equipment, but systematic and automated production solutions that enhance our customers' global competitiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main advantage of CNC over traditional glass processing methods?
The primary advantage is unparalleled precision and repeatability. CNC machines eliminate human error from manual cutting and shaping, ensuring every piece is identical. They also enable the production of highly complex designs that are impossible or prohibitively expensive to make manually, significantly increasing productivity and reducing material waste.
2. Can CNC machines process different types of glass?
Yes, modern CNC Glass Processing Equipment can handle a wide variety of glass types, including annealed glass, tempered glass, laminated glass, and even coated or low-E glass (with specific process adjustments). The key is using the correct diamond tooling, spindle parameters, and cooling methods suited for each material's hardness and properties.
3. What are the essential safety features to look for in a CNC glass cutter?
Critical safety features include:
- Fully enclosed interlocked guarding that stops the machine when opened.
- Emergency stop buttons at multiple accessible locations.
- Automatic tool breakage detection systems.
- Efficient dust and coolant extraction systems to maintain a clean and safe workshop environment.
- Software limits to prevent axis over-travel and collisions.
4. How does the choice of diamond tool affect the processing outcome?
The diamond tool (its bond, grit size, and concentration) is arguably the most critical consumable. A harder bond lasts longer but may glaze; a softer bond wears faster but cuts more freely. Coarse grits remove material quickly for roughing, while fine grits are for finishing and polishing. Selecting the wrong tool can lead to poor edge quality, rapid tool wear, and even glass breakage.
5. Is it difficult to program and operate a CNC glass processing machine?
While the underlying technology is sophisticated, modern user interfaces have made operation more accessible. Most machines use graphical CAD/CAM software where operators import designs, define tool paths visually, and simulate the process. Training is essential, but manufacturers like Jiangyin Jingang provide comprehensive training to ensure operators can program and run the machine efficiently. For complex tasks like shaped glass edging with CNC technology, advanced programming skills are beneficial.
References
[1] Lumley, R. M. "Advanced Cutting Techniques for Brittle Materials." Journal of Materials Processing Tech, vol. 209, no. 15-16, 2009, pp. 5781-5790. (This reference supports the claim about laser-assisted cutting reducing edge chipping).
[2] Chen, H., & Wang, J. "Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Machining of Glass Substrates." Precision Engineering, vol. 42, 2015, pp. 287-293. (This reference supports the claim about ultrasonic machining reducing subsurface damage).


 English
English  русский
русский  Español
Español